Medical imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Among the most common imaging techniques are PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans and CT (Computed Tomography) scans.
While both are used to examine the body’s internal structures, they serve different purposes and use distinct technologies. This article compares and answers the question is pet scan and ct scan different, their advantages, and when each is preferred.
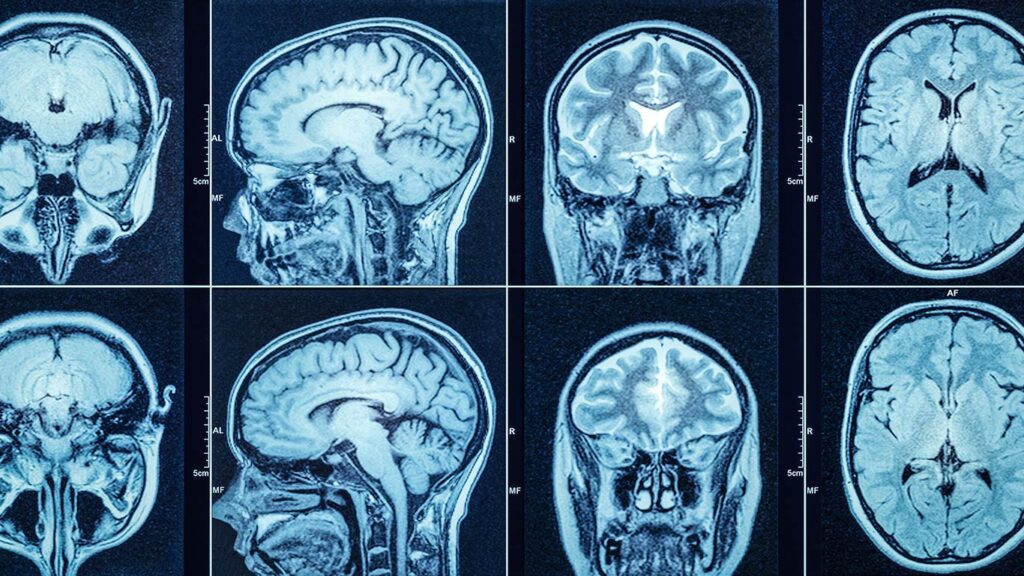
Understanding PET Scans and CT Scans
Medical professionals often recommend imaging scans based on the specific condition they are trying to diagnose. While CT scans provide highly detailed anatomical images, PET scans excel in detecting functional changes at a molecular level.
Understanding these differences can help patients and caregivers make informed decisions regarding the most appropriate diagnostic tool for their needs. The choice between PET and CT scans can significantly impact diagnosis accuracy and treatment planning, making it essential to know when each is the best option.
What is a PET Scan?
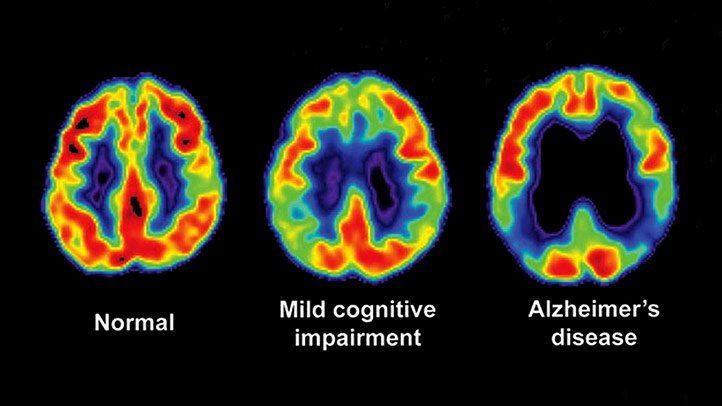
A PET scan is an advanced imaging technique that provides functional information about tissues and organs. It works by injecting a small amount of a radioactive tracer into the body. The tracer helps in detecting metabolic activity and is particularly useful for identifying cancer, brain disorders, and heart conditions. PET scans are often used in oncology to determine the stage of cancer and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It is commonly used to detect fractures, tumors, infections, and internal injuries.
Unlike PET scans, which focus on cellular activity, CT scans provide clear images of anatomical structures. Physicians often use CT scans in emergency situations to assess trauma-related injuries or detect internal bleeding quickly.
Major Differences Between PET Scans and CT Scans
| Feature | PET Scan | CT Scan |
| Purpose | Evaluates metabolic activity | Provides detailed structural images |
| Technology Used | Uses a radioactive tracer to highlight functional changes | Uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images |
| Best For | Detecting cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders | Identifying bone fractures, tumors, infections, and internal injuries |
| Image Type | Functional imaging (shows activity) | Structural imaging (shows anatomy) |
| Radiation Exposure | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Time Taken | 30-90 minutes | 5-30 minutes |
| Use of Contrast Material | Requires a radioactive tracer | May require contrast dye for enhanced clarity |
| Availability | Less commonly available | Widely available in most hospitals |
When to Choose a PET Scan VS CT Scan?
When is a PET Scan Recommended?
- Detecting cancer and monitoring its spread
- Evaluating brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy
- Assessing heart conditions by measuring blood flow and detecting damaged tissues
- Identifying metabolic disorders
- Studying the function of organs and tissues in detail
When is a CT Scan Recommended?
- Diagnosing bone fractures and internal injuries
- Detecting lung infections and tumors
- Evaluating conditions affecting organs such as the liver, kidneys, and pancreas
- Guiding biopsies and other medical procedures
- Assessing vascular conditions such as blood clots and aneurysms
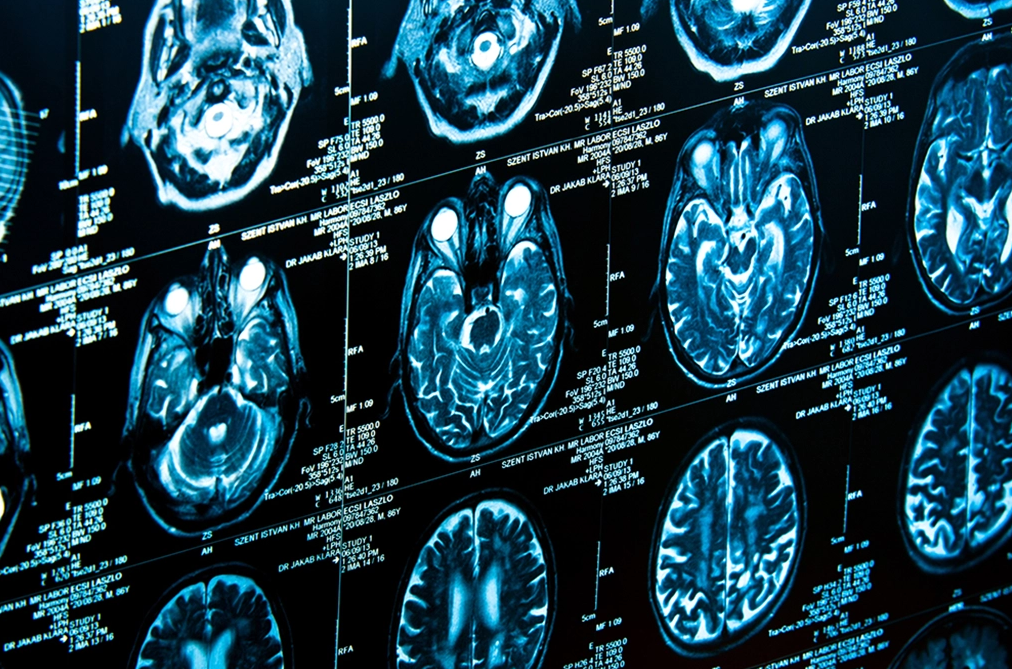
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of PET Scans
✔ Detects diseases at an early stage ✔ Provides information on cellular activity ✔ Effective for monitoring cancer treatment ✔ Helps differentiate between benign and malignant tumors
Limitations of PET Scans
✖ Higher cost compared to CT scans ✖ Requires exposure to radioactive tracers ✖ Limited availability in smaller healthcare centers ✖ Longer scan duration compared to CT scans
Advantages of CT Scans
✔ Quick and widely available ✔ Provides highly detailed structural images ✔ Useful for emergency diagnoses ✔ Helps detect internal injuries, tumors, and infections with high precision
Limitations of CT Scans
✖ Cannot assess cellular function ✖ Exposure to higher doses of X-ray radiation ✖ May require a contrast dye, which can cause allergic reactions in some individuals ✖ Less effective for detecting very early-stage cancer compared to PET scans
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a PET scan more accurate than a CT scan?
A PET scan is more effective in detecting functional changes at the cellular level, while a CT scan provides clearer anatomical details. The choice depends on the condition being evaluated.
Does a PET scan detect cancer better than a CT scan?
Yes, a PET scan is better at detecting cancer spread and distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors, whereas a CT scan is useful for locating abnormal growths.
Are there any risks associated with PET and CT scans?
Both scans involve radiation exposure. PET scans use a small amount of radioactive tracer, while CT scans use X-rays. Pregnant women and individuals with kidney problems should consult their doctor before undergoing these tests.
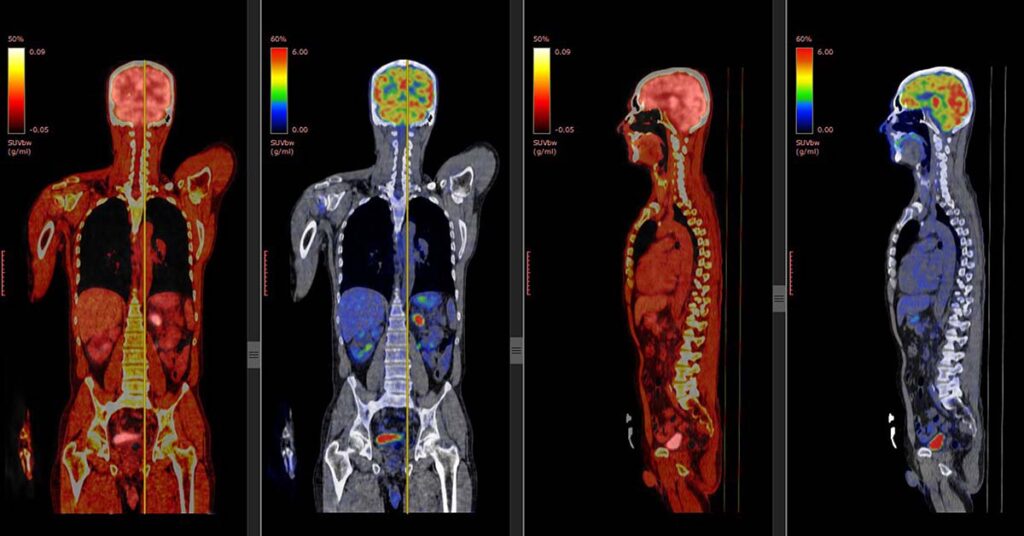
Can PET and CT scans be combined?
Many medical facilities offer PET-CT scans, combining both techniques to provide comprehensive diagnostic information in a single session. This approach allows for both functional and structural analysis, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Which scan is more expensive?
PET scans are generally more expensive due to the use of radioactive tracers and specialized imaging technology. CT scans are more affordable and widely accessible.
Closure
Both PET and CT scans play important roles in medical imaging but serve different purposes. A PET scan is best for detecting functional abnormalities, such as cancer progression and brain disorders, while a CT scan is ideal for detailed structural imaging of bones, organs, and internal injuries.
Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine which scan is most suitable based on the medical condition being assessed. Understanding these differences ensures better decision-making and more effective diagnosis and treatment strategies.
